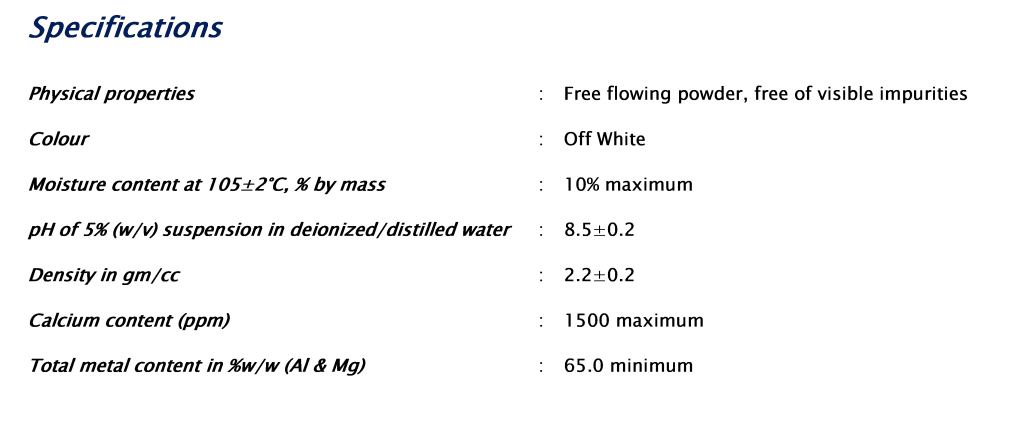MetalPlex
The Thixotropic Rheological properties of Mixed Metal Oxide/Hydroxide Systems have long been considered a solution to highly challenging drilling environments. Challenges include Formations prone to lost circulation, unconsolidated formations, high angle drilling, extended reach wells etc. MetalPlex is our proprietary Single Sack, High Performance Mixed Metal Complex (MMH-MMO) additive for Water Based Drilling Systems. It is a highly economical system in Hard Rock as well as Unconsolidated Formations. The additive has been specially engineered to be Tolerant of Anionic Additives and contaminants. It has High Shear Thinning, Temperature Stability upto 165°C, Low Plastic Viscosity and High Static Gel Strengths. The low Calcium content improves Gelation values to increase compatibility with Carbonate Formations and Restricts Progressive Gelation.
Advantages of the MetalPlex System:
- Faster Drilling in Loss Zones with built in Loss Control Remedy
- Reservoir/Non-Reservoir compatibility
- Possibility of Eliminating Casing Strings
- Strict Control on NPT
- Environmentally Friendly Green Solution
- Higher Carbon Credits
- Can be Formulated in Fresh Water, Saline Water or Sea Water to 30,000 ppm
- Temperature range of 70-160°Celcius
Case Histories
Our MetalPLex system has been applied with astonishing results in combatting the above challenges. A few notable accomplishments are as follows:
- A major operator was able to drill a subsea completion well hitherto considered one of the most challenging types of wells, with acceptable losses. The pore pressure encountered was 5.6 – 6.0 ppg whereas wellbore stability required 9.6 – 9.8 ppg mud. The well was successfully drilled with ~9.8 ppg mud, without encountering losses. The system was used to drill the pay zone and a production rate of ~ 170,000/- M3of gas/day evidenced the fact that there was little to no formation damage during drilling.
- A major operator has drilled several wells covering multiple formations with varied pore pressures, in a single section. The formations included fractured shale and limestones. Some of the zones encountered were pay zones which after prolonged production have become sub-hydrostatic. These zones have a pore pressure of 5.0 – 6.0 ppg, the intermediate section has a pore pressure of ~ 9.0 ppg, and the target zone has a pore pressure of ~ 8.3 ppg. All these formations were drilled as a single section of 300-400m with mud weights ~ 10.2 ppg successfully, with acceptable mud losses and no hole collapse issues. Offset wells of similar construction routinely experience mud losses to the tune of 110,000/- bbls in this section.